Congratulations to Novo Nordisk for their new article using EndoC-βH5®, a model similar to human native beta cells with unlimited quantity, in their innovative large-scale functional genomics screen in DM research
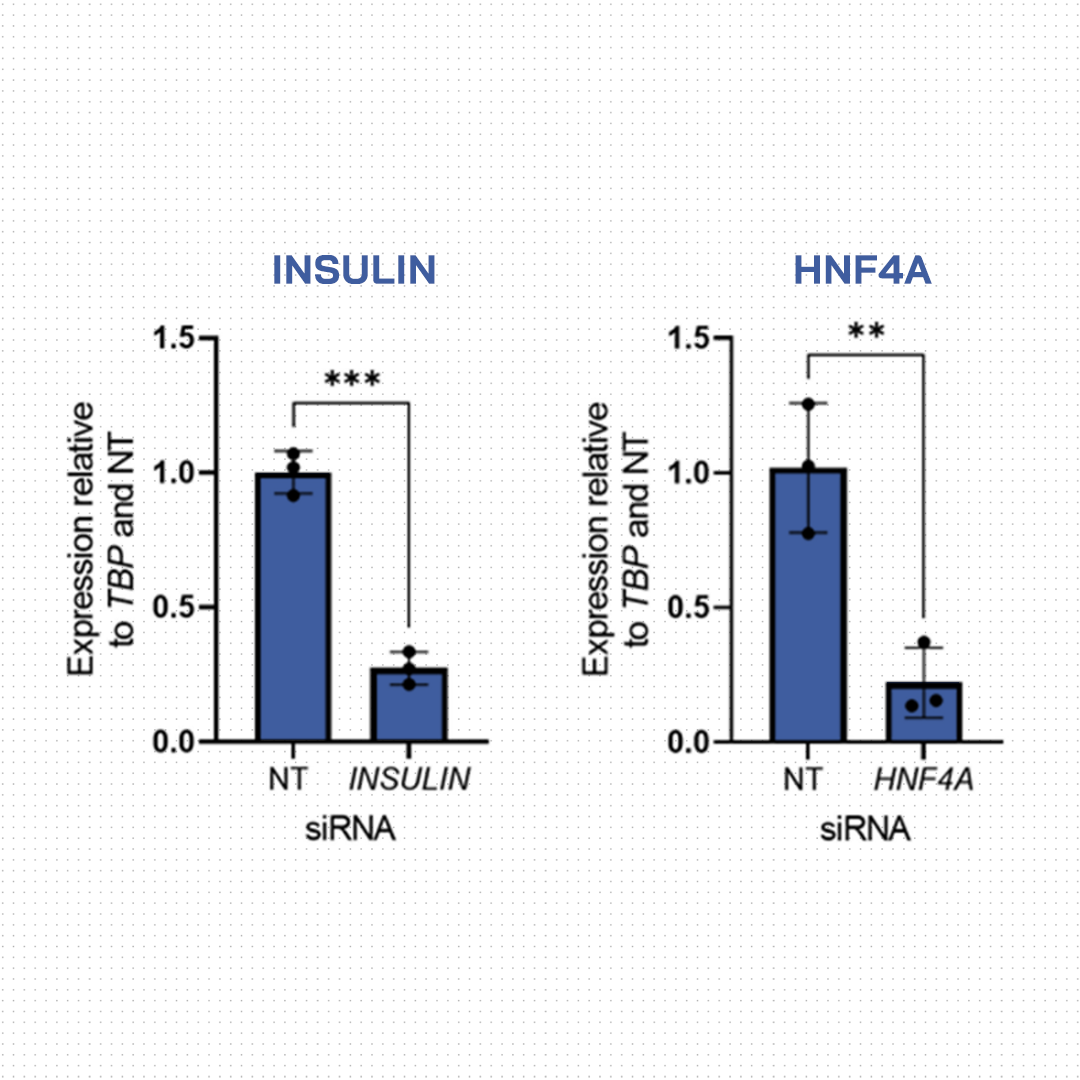
Using the EndoC-βH5® model, a team of researchers at Novo Nordisk Research Centre in Oxford validated novel genes regulating human β-cell insulin secretion.
![]() Established a 384-well functional screen
Established a 384-well functional screen
![]() Used disease-relevant insulin secretion endpoints
Used disease-relevant insulin secretion endpoints
![]() Successfully applied siRNA-mediated loss-of-function
Successfully applied siRNA-mediated loss-of-function
![]() Identified potential T2D drug targets
Identified potential T2D drug targets
Novo Nordisk research center identified novel modulators of insulin secretion and potential T2D drug targets and concomitantly demonstrated the relevance and applicability of the Endoc-BH5® model in miniaturized large scale and high throughput genomic screens that use disease relevant endpoints, i.e glucose and GLP1-R induced insulin secretion.
Endoc-BH5® is a human beta cell models which represents a robust option for bridging the gap between using primary beta cells based solutions drawbacks in term of variability, time consuming, cell modeling and reactivity as a full ready to use frozen solution you can store and use freely when you need it!
Szczerbinska I, Tessitore A, Hansson LK, Agrawal A, Ragel Lopez A, Helenius M, Malinowski AR, Gilboa B, Ruby MA, Gupta R, Ämmälä C. Large-Scale Functional Genomics Screen to Identify Modulators of Human β-Cell Insulin Secretion. Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 4;10(1):103. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010103. PMID: 35052782; PMCID: PMC8773179.
Read the whole article >>>
Comments are closed.





